Nano Research(JCR Q1,IF: 8.897) published online the latest review of our college entitled "Engineering DNA quadruplexes in DNA nanostructures for biosensor construction" (http://www.thenanoresearch.com/work_just.asp?page=10). Prof. Junqing Hu and Dr. Shiliang He were co-corresponding authors. Dr. Jingxin Liu and Dr. Li Yan were the co-first authors.
Differentfrom the well-known double helix, DNA quadruplexes are nucleic acid conformations comprised of four strands. They are prevalent in human genomes. Because their formation exhibits strong reliance on the environment, increasing efforts are being directed toward their engineering into stimuli-responsive nanomachine modules. On the other hand, taking advantage of the programmability of Watson-Crick base-pairing and conjugation methodology of DNA with other molecules, DNA nanostructures of increasing complexity and diversified geometries have been artificially constructed since 1980s.
Inthis review, the authors investigated the interweaving of natural DNA quadruplexes and artificial DNA nanostructures in the development of the ever-prosperous field of biosensing (Figure 1), highlighting their specific roles in the construction of biosensor, including recognition probe, signal probe, signal amplifier and support platform. Their implementation in various sensing scenes is surveyed. And finally, general conclusion and future perspective are discussed for further developments.
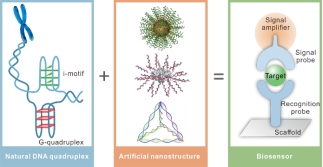
Figure 1.Biosensor construction using natural DNA quadruplexes and artificial DNA nanostructures.